The software includes the following single pile capacity calculation methods:
1.AV method (Aoki & Velloso, 1975)
2.DQ method (Décourt & Quaresma, 1978 and Décourt 1996)
3.PFM method (Monteiro, 2000)
For all the above mentioned methods, pile bearing capacity (Q) for a closed ended pile is assumed to be the sum of :
Q = Qtip + Qshaft
Qtip = Atip × q
Qshaft = ∑ U ƒ dL
where:
Qtip: Pile tip resistance
Qshaft: Pile shaft resistance
q: Unit tip resistance
ƒ: Pile shaft unit friction
Atip: Pile tip area
U: Pile perimeter
L: Pile length
AV and PFM methods
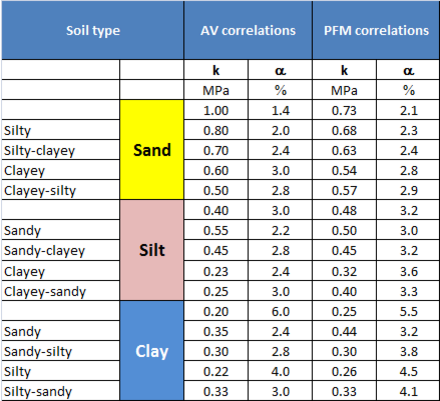
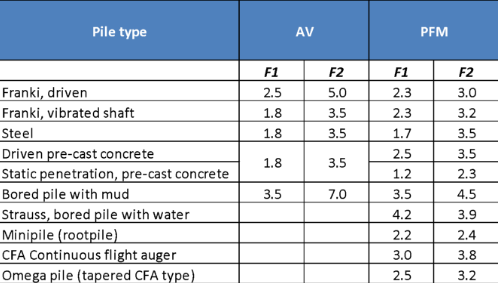
Unit tip resistance q is calculated using the following formula:
q = k × N / F1
and shaft unit friction is calculated according to:
ƒ = α × k × N / F2
Values of k and α depend on soil and pile type. N is the uncorrected SPT value at a given depth of calculation. The following tables present the empirical coefficients for tip resistance q and shaft friction ƒ as a function of soil type.
DQ method
Unit tip resistance q is calculated using the following formula:
q = α × Κ × N
where the SPT value N at a given depth z is the mean value obtained at three depth levels: z-1, z and z+1. The average shaft unit friction is calculated according to:
ƒ = β × [(Nm/3) + 1]
where Nm at a given depth z is obtained from the SPT value at depth z-1. For this method the following limits apply:
•If N < 3 then consider N = 3
•If N > 50 the consider N = 50
The following tables present the empirical coefficients for tip resistance q and shaft friction ƒ as a function of soil type.


Limits to be considered
1. N values should not be greater than 50
2.The structural capacity of the pile (given value)
3.Micropiles in rocks may be analysed with N = 50 and it is recommended to consider shaft resistance only
4.Limits for micropiles unit values: q = 5 MPa, f = 250 kPa
5.Bored piles should limit the tip resistance calculated by these correlations. In general it is recommended that the pile tip resistance should be only 20% to the pile capacity. If the pile tip is cleaned with air-lift to remove soil cuttings or soil plug, this value can be raised to 35%